vascularsurgery 2021
About Conference
Euroscicon LTD with immense pleasure invites all the contributors across the globe to our Webinar on 7th Edition of World Congress & Exhibition on Vascular Surgery during November 15-16, 2021 which includes prompt keynote presentations, oral talks, poster presentations and exhibitions. Euroscicon LTD organizes 1000+ scientific events inclusive of 600+ conferences, 500+ workshops and 200+ symposiums on various topics of science & technology across the globe with support from 1000 more scientific societies and publishes 500+ open access journals which contain over 50000 eminent personalities, reputed scientists as editorial board members.
Vascular surgery deals with the diagnosis and sub-surgical procedures for the management and treatment of disorders/diseases related to the vascular system, i.e. veins, arteries and the lymphatic system, excluding the coronary and intracranial arteries. A vascular surgeon is concerned with treating the blood vessels of the body including arms, legs, organs and other tissues of the body, except that of heart and brain. Vascular surgery is advised when a vascular disease cannot be treated by less invasive or non-surgical methods. The purpose of vascular surgery is to treat those diseases related to veins and arteries known as arterial and venous diseases.
Vascular diseases are caused due to the conditions like clotting of blood in blood vessels, weaken blood vessels or damaged valves which control the flow of blood within the veins thus depriving of vital nutrients and oxygen. Common vascular diseases are atherosclerosis, aortic aneurysms, peripheral vascular disease, carotid artery disease. Surgery is often suggested to treat such diseases to aid prevent strokes or heart attacks, relieve angina or hypertension, eradicate aneurysms, improve claudication by repairing the arteries, bypassing, or replacing them. Atherosclerosis i.e., the hardening of arteries occurs as people age due to the accumulation of fatty material containing cholesterol or calcium on the innermost layer of artery; cause the narrowing of the inside diameter of the blood vessels. Gradually, the blood vessels become so narrow that blot clots (thrombus) forms which blocks the blood flow to the entire portion of the body; creating the condition known as PVD or peripheral arterial disease. In another form of atherosclerosis, ulcer forms in the diseased interior of the blood vessels where blood clots tend to form. These blood clots then break the ulcer and block the arteries in the narrower ends.
Vascular surgery involves techniques relating to endovascular surgeries such as balloon angioplasty with or without stenting, aortic and peripheral vascular graft replacement, thrombolytic therapy, and other aides for vascular reconstructions.
Target Audience
The target audience will be mostly Vascular Surgeons and Residents but also General Surgeons, Angiology Specialists, Phlebologists, Interventional Radiologists, Vascular Medicine Specialists, Dermatologists, Nurses, Technicians and all others interested in the management of venous and arterial diseases.
Sessions/Tracks
Track 1: Vascular Trauma
The term ‘vascular trauma’ refers to damage or injury to a blood vessel- an artery, which carries blood away from the heart, or a vein, which carry blood back to the heart from different organs. These injuries are categorized by the type of trauma that cause them: blunt or penetrating injury.
• Blunt injury can occur if a blood vessel is crushed or stretched.
• penetrating injury can occur if a blood vessel is punctured, torn or severed.
Both the types of vascular trauma can cause the blood vessel to clot (thrombosis) and interrupt blood flow to an organ, or cause bleeding, leading to life-threatening hemorrhage.
Vascular trauma results from a wide range of causes:
Injury (accidents, falls, cuts, etc.)
Violence
Pinching of a vein or artery
Dislocation of a bone
Piercing of a vein, such as with insertion of an IV.
Vascular injury has two main consequences- hemorrhage and ischemia. Unrecognized and uncontrolled hemorrhage can lead to demise of the trauma patient while unrecognized and untreated ischemia can lead to stroke, limb loss, bowel necrosis and multiple organ failure.
Track 2: Venous Surgery
Chronic Venous Insufficiency and Varicose veins are the most frequent blood vessel abnormalities occurring in people and affects approximately one third of the population. The treatment of these disorders depends on many factors. Mild and moderate symptoms can be successfully treated with the use of compression stocking therapy but for severe symptoms medical surgeries are done either to remove varicose veins or to close them which includes: Vein stripping, Vein ablation, Sclerotherapy, Laser Surgery, Endoscopic Vein Surgery, Ambulatory Phlebectomy.
Track 3: Vascular Diseases of the Lower Limbs
Vascular diseases of the lower limb include: Peripheral Arterial disease of the legs and Chronic Arterial Insufficiency of the lower extremities. PAD is the condition of blood vessels that supply the legs and feet. It includes the narrowing and hardening of the arteries that results in decreased blood flow, which can injure nerve and other tissues. This problem occurs due to the buildup of fatty material (plaque) on the inside wall of arteries. Plaque is made up of extra cholesterol, calcium in blood. Blood carries the oxygen to the lower extremities but plaque buildup starves the tissues and muscles in lower limb. The underlying mechanism is usually atherosclerosis. The main risk factors include cigarette smoking, diabetes, high blood cholesterol and high blood pressure.
Track 4: Carotid Artery Disease
The carotid arteries are the blood vessels (coronary arteries) that carry oxygenated blood to the head, brain and face. They are located on each side of the neck. These arteries supply oxygen-rich blood to the large front part of the brain which control thought, personality, speech, as well as our sensory and motor functions. Carotid Artery disease occurs due to the narrowing of these arteries mostly due to atherosclerosis (plaque buildup). These plaques may break and block smaller arteries in the brain. The arteries are the source of oxygenated blood to the brain but this blockage interrupts the blood flow thus increasing the risk of stroke. A stroke can cause lasting brain damage, long-term disability, such as vision, speech problems or paralysis; or death.
Track 5: Vascular Disease of Upper Limb
Upper extremity vascular disease is relatively uncommon compared to lower extremity vascular disease but represents a unique diagnostic challenge for the physicians. The most common causes of upper extremity vascular disease are atherosclerosis and Embolic disease, but there are other systemic diseases and anatomic abnormalities such as vasculitis, arteritis, Takayasu’s Arteritis, Thoracic Outlet Compression Syndrome, Acute occlusive arterial disease and Aneurysm of upper limb artery. Some of the typical symptoms of upper extremity vascular disease include: discomfort or pain in arms, tightness, heaviness, weakness or cramping in one or both arms.
Track 6: Abdominal Aortic Aneurysms
An Abdominal Aortic Aneurism (AAA) is an enlarged area in the lower part of the aorta- the major blood vessel that supplies blood from the heart up to head and arms and down to abdomen, legs and pelvis. As aorta is the body’s main supplier of blood, a ruptured abdominal aortic aneurysm can cause life threatening bleeding. Large aneurysms are rare but are usually fetal. The bulging occurs when the walls of the aorta weakens. The reason of weakness is thought to be smoking, high blood pressure, high cholesterol level. Rupture of the abdominal aorta may result in pain in the abdomen, low blood pressure or loss of consciousness and often results in death. AAA most commonly occurs in men over 50 years of age and among those with a family history. Surgery is normally recommended with enlarged AAA, and repair may be either by open surgery or Endovascular Aneurysm Repair (EVAR).
Track 7: Thoracic Aortic Vascular Surgery
Thoracic Aortic Aneurysm is an expansion or ballooning of a section of aorta within the chest (thorax) that slowly degenerates. Thoracic Aortic Aneurysms are rare, occurring in approximately 6-10 per every 100,000 people. Surgery is often suggested if the risk of rupture is higher. The procedure for Thoracic Aortic Vascular Surgery is called Thoracic Endovascular Aortic Repair (TEVAR). To fix the aorta, a device made of a fabric- covered metal mesh known as stent graft is inserted through a small hole. The device repairs the diseased aorta, helps to keep it open and allows blood to flow easily to rest of the body. The alternative to TEVAR is refer to as ‘open repair’, which requires a large incision through the breastbone or side of the chest.
Track 8: Thoracoabdominal Aortic Vascular Surgery
Thoracoabdominal Aortic Aneurysm (TAAA) refers to the abnormal widening of the aorta involving both the thoracic and abdominal segments. These aneurysms are primarily the results of age related degeneration and weakening of the aortic wall. Elective surgical interventions are considered when the aortic size exceeds 5-6 cm. There are three surgical operative techniques for TAAA repair: open, endovascular and hybrid.
Open TAAA repair involves surgical removal of the diseased section of the aorta and replacing it with an artificial graft by making an incision extending from the upper back on the left side, curving around under the shoulder blade around to the front of abdomen.
Endovascular approach includes much less invasion with small incisions to access the blood vessels in the groin. A catheter is inserted and is used to deploy a stent graft within the aneurysm.
Hybrid approach uses a combination of the two techniques.
Track 9: Surgery for Veins and Lymphatic Diseases
Thrombolytic therapy, surgical thrombectomy, and placement of inferior vena cava filters are adjunctive treatments that can be suggested for patients with extensive and complicated venous thromboembolism. For patients with saphenous vein valvular insufficiency vein stripping, endovenous laser treatment and radiofrequency ablation therapies are implemented. Concomitant varicose veins may be managed with compression therapy, sclerotherapy and phlebectomy.
Track 10: Vascular Imaging
Vascular imaging is a test that enables to access and evaluate the body’s circulatory system and help identify blockages in veins and arteries and detect blood clots. Non-optical methods that are widely used for vascular images includes X-ray/CT, MRI, ultrasound and positron emission tomography. These techniques are most popularly used for macrovascular imaging but due to poor spatial contrast these are not effective for microvascular imaging. Optical methods recommended for microvascular imaging are single-photon fluorescence microscopy (1PFM), two-photon fluorescence microscopy, orthogonal polarization spectral imaging (OCSI), laser speckle contrast imaging (LSCI), diffusive imaging, diffuse optical tomography, etc.
Track 11: Vascular Malformations
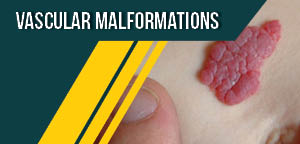
Vascular malformations are abnormal clusters of blood vessels that occur during fetal development. These malformations are thought to result from developmental errors during embryogenesis such as abnormal signaling processes that control apoptosis, maturation and growth of vascular cells. Although these kinds of lesions are present at birth, they may not be visible until weeks or several years but typically grow in proportion to the growth of the child. Vascular malformations are characterized under four types based on their flow characteristics: slow flow (capillary malformations, venous malformation, lymphatic malformation) and fast-flow (arteriovenous malformation). Proper identification and multidisciplinary approach is paramount for proper treatment.
Track 12: Acute Limb Ischaemia/Limb Ischaemia

Acute limb ischaemia is defined as a sudden decrease in limb perfusion that results in potential threat to the viability of the limb. It results from a sudden obstruction in the arterial flow mainly due to embolism or thrombosis and rarely by dissection or trauma. The occurrence of this case is almost 1.5 cases per 10,000 persons per year. Symptoms begins over a period of hours or days from new or worsening intermittent claudication to pain in foot or leg, muscle weakness, and paralysis of the affected limb. The rapid onset of limb ischemia results from sudden blockage of blood supply and nutrients to tissues and nerves of the limb; threatening limb viability due to insufficient time for new blood vessel growth to compensate for loss of perfusion. The primary intervention for acute limb ischemia is emergency embolectomy or vascular bypass to route the blood flow.
Track 13: Renovascular Surgery
Renal artery is the vessel through which blood passes to the kidney to remove the body’s waste. These renal arteries originate in the heart and are also responsible for carrying oxygenated blood to the kidneys. Like other arteries the renal arteries also become blocked, the condition which is called renal artery stenosis. These arteries are affected due to several diseases such as atherosclerosis, renal artery aneurysm, fibromuscular dysplasia and vasculitis. Decreased blood flow to the kidneys often lead to hypertension. If untreated, renovascular hypertension may lead to cardiovascular and kidney problems. Treatments for renovascular hypertension refer to restore the normal blood flow to the kidney. This may be done by balloon angioplasty, use of stent to keep the artery open. Surgical technique in case of atherosclerosis include endarterectomy or bypass grafting.
Track 14: Mesenteric Ischemia

Mesenteric Ischemia is a condition caused by poor blood supply to the small intestine, colon or both and eventually results in gangrene of the bowel wall. It may also affect other organs in the digestive system. Due to poor circulation blockages may form that compromises the function of those organs. Mesenteric ischemia has both acute and chronic forms. Acute ischemia seeks a surgical emergency. It is associated with both embolic and thrombotic occlusions. 40-50% of the cases are related to embolic occlusions whereas 20-35% of the cases are due to thrombotic occlusions. Mesenteric ischemia is rare but is potentially a life-threatening condition. Treatment is by embolectomy, revascularization of viable segment or resection and sometimes vasodilator therapy is successful.
Track 15: Congenital Diseases of Vasculature
Congenital vascular anomalies are rare. Congenital vascular anomalies occur in barely 1% of all births. These are the vascular malformations or vascular tumors i.e., abnormally formed blood vessels present by birth. Congenital vascular diseases include vascular malformations and vascular tumor known as hemangioma; both of which are commonly called “birthmarks”. Most of these birth marks represent vascular malformation, consisting of abnormal collection of small blood vessels near the skin. Normally vascular malformations are not a health threat as they grow proportionately with the growth of the child. But hemangioma may be alarming during their growth phase called the ‘juvenile hemangiomas’ and requires immediate treatment.
Track 16: Lymphedema

Lymphedema, or lymphatic obstruction, is a long-term condition where excess fluid collects in tissues causing swelling (edema). The main symptom is swelling in arm, or leg that may be accompanied by pain or discomfort. Lymph is a clear, thin fluid that circulates throughout the body to remove wastes, bacteria, and other substances from tissues. Edema is the buildup of excess fluids. So, lymphedema occurs when too much lymph gets collected in an area. The cause of lymphedema is generally cancer treatment where one or two lymph nodes are removed. Normally lymph nodes filter fluids that flow through them, so without normal lymph drainage, fluid can build up in the affected arm or leg and lymphedema develops. Lymphedema can also be present by birth or can develop during puberty.
Track 17: Venous Insufficiency

Venous insufficiency is a condition where the flow of blood in the veins is inadequate, which causes blood to pool in the legs. In these states valve in the veins don’t work and venous blood refluxes backward down the veins into an already congested leg. Chronic venous insufficiency is a long-term condition. It is commonly due to malfunctioning (incompetent) valves in the veins. It may also result from the blood clot in the veins. Usually it is treated by compression stockings, exercise and weight loss, but in some cases, require vein ablation or vein stripping.
Track 18: Vascular Bypass Grafting
Bypass grafting is a surgical procedure to redirect blood flow from one area to another in an area of blockage by reconnecting vessels. It is performed due to ischemia (inadequate blood flow) caused by atherosclerosis or other vascular diseases. In this procedure, an alternate channel is created for blood flow by replacing a damaged vessel. The graft is generally taken from one’s own healthy region (autograft), or a graft material such as Teflon or Dacron. The lifespan of a surgical bypass depends on the health of the arteries, the type of graft used- natural vein graft last longer than synthetic ones.
Track 19: Techniques of Open Vascular Surgery
Some of the open vascular surgeries are:
Arterial graft- it is performed to bypass a diseased or blocked part of an artery in order to restore proper blood flow and reduce the risk of complications. The graft is taken from healthy part of the body such as arms or legs.
Carotid endarterectomy- it begins with an incision in the neck, exposing the narrowed carotid artery where the surgeon opens the artery to remove the plaque.
Surgical aneurysm repair- aneurysm is an abnormal bulge in the wall of an artery, they are extremely risky: if they burst it can lead to life threatening internal hemorrhage. Open aneurysm repair includes replacement of weakened part of the artery with a tube-like structure.
Abdominal aortic aneurysm surgery- It involves the incision to open the abdomen, removing the aneurysm and replacement of the excised portion with synthetic tube.
Track 20: Anesthesia for Vascular Surgery
A vascular surgical procedure can be performed under local, regional or a general anesthesia, or a combination of these techniques based upon the complexity of the vascular pathology. Anesthesia is a risk factor which contributes to perioperative morbidity and mortality of vascular patients. Minimally invasive approaches to vascular surgery are developing gradually allowing the use of more localized anesthesia. It is often supposed that undergoing a procedure with local or regional anesthesia results in lower mortality and morbidity and results in earlier recovery.
Track 21: Lower Limb Amputations
Lower limb amputation in relation to vasculature means the surgical removal of leg or foot from the body as a result of peripheral vascular diseases. It is a life-saving procedure done to remove ischemic, infected, or necrotic tissue. Peripheral arterial diseases alone or in combination with diabetes mellitus contributes to more than half of the amputations. Major amputations are due to PAD ranging from 12 to 50 per 100,000 individuals per year.
Track 22: Endovascular Surgery
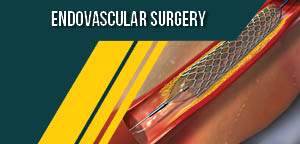
Endovascular surgery is used to treat vascular diseases from inside the blood vessels. A small incision is created to gain access to the diseased area (veins and arteries) inside the body. This technique results in less pain and faster recovery. These are the minimally invasive techniques to repair vascular aneurysms with the help of intravascular sheaths, wires, catheters, balloons, stents and stent grafts. The most common and advanced form of endovascular surgery going on today is an endovascular repair of aortic aneurysms and dissections by use of stent grafts inserted into vasculature via arteries in the groin.
Track 23: Vascular Cell & Molecular Biology
The Vascular Cell and Molecular Biology section define applications that involve cell and molecular biology of blood vessels ranging from major arteries to the microcirculation. This section includes studies that involve cellular, biochemical, biophysical, immunological, genetic, pharmacological, and molecular biological approaches to define vascular homeostasis and dysfunction. A principal focus is on the biology of the endothelium and vascular smooth muscle cells, their role in vascular diseases; molecular genetics of vascular and arterial diseases; Vascular dysfunction, including endothelial barrier function, blood-brain barrier and arterio-venous malformations; Injury/repair; remodeling; angioplasty; restenosis; grafts; stents; re-endothelialization; stem cells.
Market Analysis
Global Vascular Surgery Minimally Invasive Surgical Instruments market is a growing market in Healthcare, Pharmaceuticals sector at present years. The Vascular Surgery Minimally Invasive Surgical Instruments has uncovered rapid development in the current and past years and is probably going to proceed with a continuing development in the upcoming years.
The minimally invasive surgical instruments market is projected to reach USD 21.47 Billion by 2021 from USD 13.89 Billion in 2016, at a CAGR of 9.1%. Benefits of minimally invasive surgeries over traditional open surgeries; reduction in healthcare costs and time; increasing number of surgeries among the aging population; increasing prevalence of lifestyle disorders; and technological advancements are key factors expected to drive the growth of the market. Increasing awareness of technologically advanced MIS instruments & procedures and emerging markets provide significant growth opportunities for the market.
This report segments the global minimally invasive surgical instruments market by product, application, end user, and region. The global market, by product, includes handheld instruments, electrosurgical instruments, inflation systems, guiding devices, auxiliary instruments, and cutter instruments. In 2015, the handheld instruments segment accounted for the largest share of the global market. These instruments are convenient to use and are widely implemented in almost all kinds of MIS surgeries; these factors contribute to their largest share in the MIS instruments marketWorldwide Vascular Surgery Minimally Invasive Surgical Instruments market is predominantly classified on the basis of leading marketing players, product types, applications and worldwide regions covering North America, South America, Africa and Middle East, Europe and Asia-Pacific
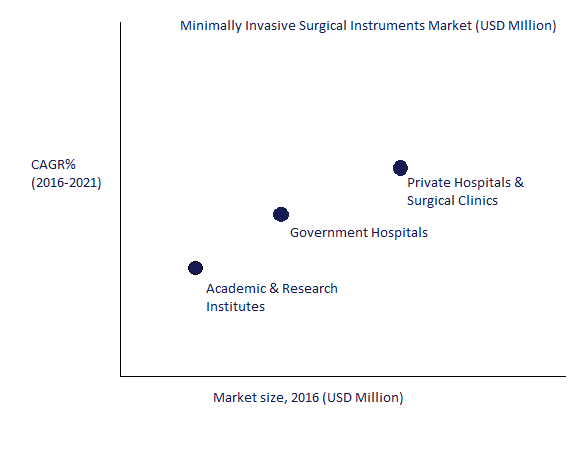
On the basis of end users, the global minimally invasive surgical instruments market report is segmented into government hospitals, private hospitals & surgical clinics, and academic and research institutes. In 2015, the private hospitals and surgical clinics segment accounted for the largest share of the global market. The growth of this end-user segment can be attributed to the high hygienic standards of private hospitals, low chances of contracting hospital-acquired infections, presence of cutting-edge equipment and ICUs, and timely check-ups. Therefore, the increasing adoption of minimally invasive surgeries in private hospitals and surgical clinics will increase the usage of MIS instruments, hence leading to its growth.
The geographic segments included in this report are North America, Europe, Asia-Pacific, and the Rest of the World (RoW). North America is further segmented into the U.S. and Canada. In 2015, North America accounted for the largest share of the global minimally invasive surgical instruments market primarily due to the rising number of surgical procedures, growing government investments, growing geriatric population, and rising prevalence of lifestyle diseases in this region. With the rising geriatric population, presence of a large patient pool undergoing surgical treatments, growing awareness about modern surgical instruments and techniques, and implementation of various initiatives to reduce the rising healthcare expenditure in Asia-Pacific, the demand for minimally invasive surgical instruments in this region is expected to grow, which in turn will compel the key players to expand their geographical presence in this region.
Major players in the global minimally invasive surgical instruments market are Medtronic plc (Ireland), Ethicon, Inc. (U.S.), Aesculap, Inc. (Germany), Stryker Corporation (U.S.), and Smith & Nephew (U.K.). These players have a strong presence in major as well as emerging markets. Other players in this market are ConMed Corporation (U.S.), Abbott Laboratories (U.S.), Applied Biomedical Resources Corporation (U.S.), Microline Surgical (Japan), and Zimmer Biomet (U.S.).
Visa Information
We welcome all our participants at 6th Edition of World Congress & Exhibition on Vascular Surgery, Belgium, Brussels during April 28-29, 2021. We hope this conference will be a great platform for sharing new technologies and ideas in the field of Vascular health and treatment of Vascular diseases.
Keeping in view of increased security measures, we would like to request all the participants to apply for Visa as soon as possible. EuroSciCon Ltd. will not directly contact embassies and consulates on behalf of visa applicants. All delegates or invitees should apply for Business Visa only.
Travelling to Germany has never been more organized and stress-free no matter what the purpose of travel is. Due to Schengen Agreement reached in 1985, the citizens of the Schengen member states can travel visa free throughout the whole territory. On the other hand, nationals of non-Schengen countries are permitted to enter the whole area with one unified document known as the Schengen Visa.
When in Germany, one is allowed to visit all the other members of the Schengen Zone: Austria, Belgium, Czech Republic, Denmark, Estonia, Finland, France, Germany, Greece, Hungary, Iceland, Italy, Latvia, Lithuania, Luxembourg, Malta, Netherlands, Norway, Poland, Portugal, Slovakia, Slovenia, ,Spain,Sweden, Switzerland and Liechtenstein.
The short-stay Schengen visa allows its holders to enter and reside in Germany for a maximum period of 90 days (3 months) within a 180 days period. However, during this time one is not entitled to engage in paid activity.
According to Germany short-stay entry rules, the residents of 62 third-world countries are permitted to enter Germany visa-free and remain there for a period of 90 days within 6 months. During this period, visitors are not permitted to work, but they can engage in business.
The countries that fall under the visa-waiver program are as following:
- Albania
- Andorra
- Antigua and Barbuda
- Argentina
- Australia
- Bahamas
- Barbados
- Bosnia and Herzegovina
- Brazil
- Brunei
- Canada
- Chile
- Colombia
- Costa Rica
- Dominica
- El Salvador
- Georgia
- Grenada
- Guatemala
- Honduras
- Hong Kong
- Israel
- Japan
- Kiribati
- Macao
- Macedonia
- Malaysia
- Marshall Islands
- Mauritius
- Mexico
- Micronesia
- Moldova
- Monaco
- Montenegro
- New Zealand
- Nicaragua
- Palau
- Panama
- Paraguay
- Peru
- Saint Kitts and Nevis
- Saint Lucia
- Saint Vincent
- Samoa
- San Marino
- Serbia
- Seychelles
- Singapore
- Solomon Islands
- South Korea
- Taiwan
- Timor Leste
- Tonga
- Trinidad and Tobago
- Tuvalu
- Ukraine
- United Arab Emirates
- United States of America
- Uruguay
- Vanuatu
- Vatican City
- Venezuela
Individuals who are not a national of any of these 62 must obtain a visa first, in order to be permitted to enter Germany.
Germany Visa Requirements
The following documents are required for any Germany visa application:
- Application Form
- Passport
- Photo
- Health Insurance
- Travel Itinerary
- Proof of Financial Means
In general, a Germany short-stay visa fee is EUR 60 whereas a long-stay visa is EUR 75
Additional documents required for the most frequent purposes of Germany Visa Application:
For attending EuroSciCon Conferences the following additional documents needs to be provided:
- The official invitation copy,
- Identity of applicant,
- Purpose of journey (negotiations, meetings, event by intergovernmental organizations, consultations)
- Duration of stay
- Place of accommodation
Please note: For security purposes, letter of invitation from EuroSciCon Ltd. will be sent only to those individuals who had registered for the conference. Once your registration is complete, please contact vascularsurgery@euroscicon.info to request a personalized letter of invitation.
Past Conference Report
Surgery Conferences team hosted the “Vascular Surgery 2020”, during April 28-29, 2021 online with the theme, “New & Emerging Techniques in Vascular Surgery”, which was a great success. Eminent keynote speakers from various reputed institutions and organizations addressed the gathering with their resplendent presence.
We extend our grateful thanks to all the momentous speakers, conference attendees who contributed towards the successful run of the conference.
Vascular Surgery 2020 witnessed an amalgamation of peerless speakers who enlightened the crowd with their knowledge and confabulated on various latest and exciting innovations in all areas of Vascular Surgery.
Vascular Surgery 2020 Organizing Committee extends its gratitude and congratulates the Honorable Moderators of the conference.
Vascular Surgery team extends its warm gratitude to all the Honorable Guests and Keynote Speakers of “Vascular Surgery 2020”.
- Omar Mutlak, Imperial College London, UK
- Ottorino Del Foco, Abu Dhabi Stem Cells Center, UAE
- Vakhtang Shoshiashvili, TSMU first university clinic. Research institute of clinical medicine, Georgia
- Andres Ramon Martinez Cardozo, Universidad Nacional del Este, Paraguay
- Yopie Afriandi Habibie, Universitas Syiah Kuala, Indonesia
Vascular Surgery team is privileged to felicitate Vascular Surgery 2020 Organizing Committee, Keynote Speakers, Chairs and also the Moderators of the conference whose support and efforts made the conference to move on the path of success. Surgery Conferences team thanks every individual participant for the enormous exquisite response. This inspires us to continue organizing events and conferences for further research in the field of Vascular Surgery, Anesthesia.
Surgery Conferences team is glad to announce its “5th Edition of World Congress & Exhibition on Vascular Surgery” which will be held during April 28-29, 2021 with the theme, “New & Emerging Techniques in Vascular Surgery”. We cordially welcome all the eminent researchers, Presidents, CEO’s, Vascular Surgery researchers, industrialists, Surgeons, doctors, young scientists, Training Institutes, Young researchers, Data Management Companies, Hospital General Counsel, Legal Nurse Consultants, Manufacturing Medical Devices Companies, students and delegates to take part in this upcoming conference to witness invaluable scientific discussions and contribute to the future innovations in the field of Vascular Surgery with 20% abatement on the Early Bird Prices.
Bookmark your dates for “Vascular Surgery 2021, London” as the Nominations for Best Poster Awards and Young Researcher Awards are open across the world.